

- #Rstudio standard deviation how to#
- #Rstudio standard deviation software#
- #Rstudio standard deviation code#
- #Rstudio standard deviation professional#
#Rstudio standard deviation how to#
Free Training - How to Build a 7-Figure Amazon FBA Business You Can Run 100% From Home and Build Your Dream Life! by ASM.Psychological First Aid by Johns Hopkins University.Excel Skills for Business by Macquarie University.Introduction to Psychology by Yale University.Business Foundations by University of Pennsylvania.
#Rstudio standard deviation professional#
#Rstudio standard deviation software#
Specialization: Software Development in R by Johns Hopkins University.Specialization: Statistics with R by Duke University.Specialization: Master Machine Learning Fundamentals by University of Washington.Courses: Build Skills for a Top Job in any Industry by Coursera.Specialization: Python for Everybody by University of Michigan.Specialization: Data Science by Johns Hopkins University.Course: Machine Learning: Master the Fundamentals by Stanford.group1 group2 effsize n1 n2 magnitudeĬoursera - Online Courses and Specialization Data science genderweight %>% cohens_d(weight ~ group, var.equal = TRUE) # A tibble: 1 x 7 If the option var.equal = TRUE, then the pooled SD is used when computing the Cohen’s d. \(n_A\) and \(n_B\) represent the sizes of the group A and B, respectively.\(m_A\) and \(m_B\) represent the mean value of the group A and B, respectively.The most commonly used version of the Student t-test effect size, comparing two groups ( \(A\) and \(B\)), is calculated by dividing the mean difference between the groups by the pooled standard deviation. There are multiple version of Cohen’s d for Student t-test. paired t-test (also known as dependent t-test or matched pairs t test).two-sample t-test (also known as independent t-test or unpaired t-test).
#Rstudio standard deviation code#
We will provide examples of R code to run the different types of t-test in R, including the: T-test conventional effect sizes, proposed by Cohen, are: 0.2 (small effect), 0.5 (moderate effect) and 0.8 (large effect) (Cohen 1998). The d statistic redefines the difference in means as the number of standard deviations that separates those means.
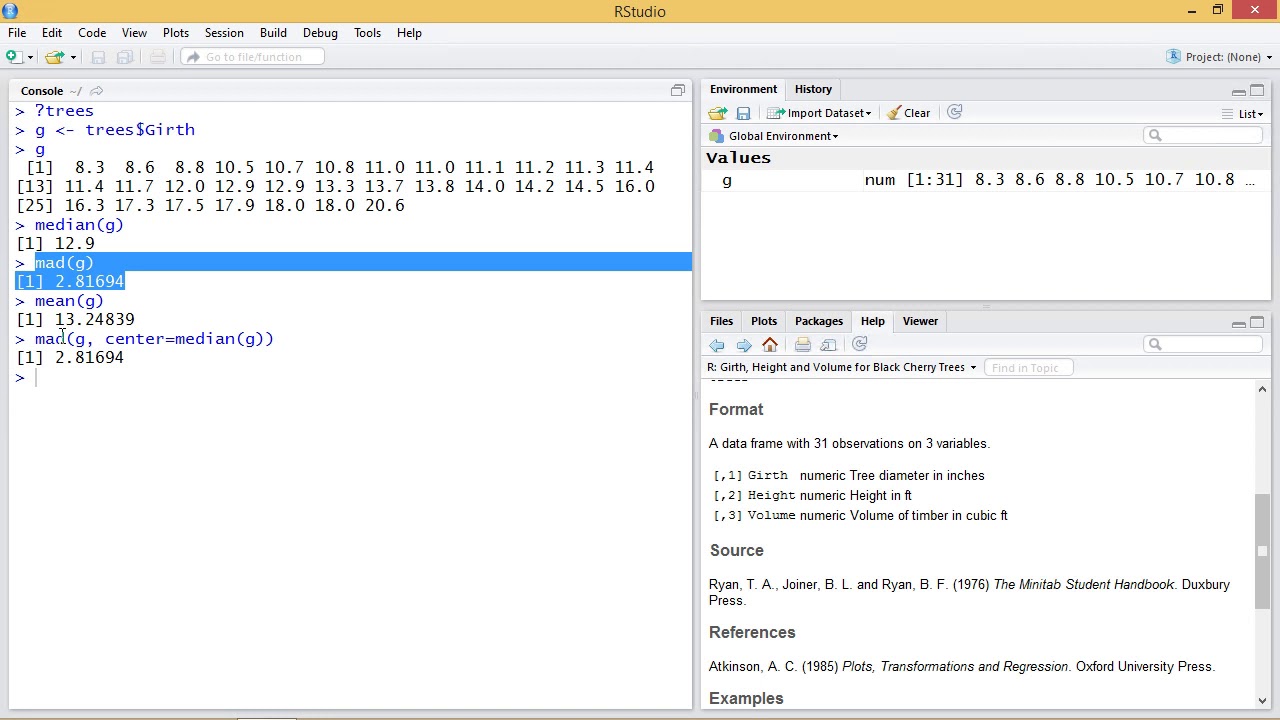
# standard deviation in R - dataset example This will help us calculate the standard deviation of columns in R. For this example, we’re going to use the ChickWeight dataset in Base R.
Need to get the standard deviation for an entire data set? Use the sapply () function to map it across the relevant items. As you can see, calculating standard deviation in R is as simple as that- the basic R function computes the standard deviation for you easily.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
